Accepting crypto payments, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, in your app opens the door to more customers in a very fast growing niche. Coinbase Commerce is like the Stripe Payments API for crypto. It provides a simple API where you can create charges, invoices, etc. But unlike credit cards, which are processed by a central authority, crypto payments are distributed to a global network of miners where they are confirmed on the blockchain. The confirmation process takes time and presents a variety of unique challenges for developers.
The following tutorial demonstrates how to accept crypto payments with Coinbase Commerce, using Firebase Cloud Functions as your backend server.
Crypto Payment Flow
Crypto payments are push-based, which means Coinbase needs to constantly listen to the payment network for changes. The API sends webhooks whenever an important event happens with a charge.
- Your server creates a charge with an amount for the user to pay. Expires after 1 hour.
- The user pays, which puts the charge in pending status (handle via webhook).
- Some time later, up to 10 minutes, charge is confirmed or failed (handle via webhook).
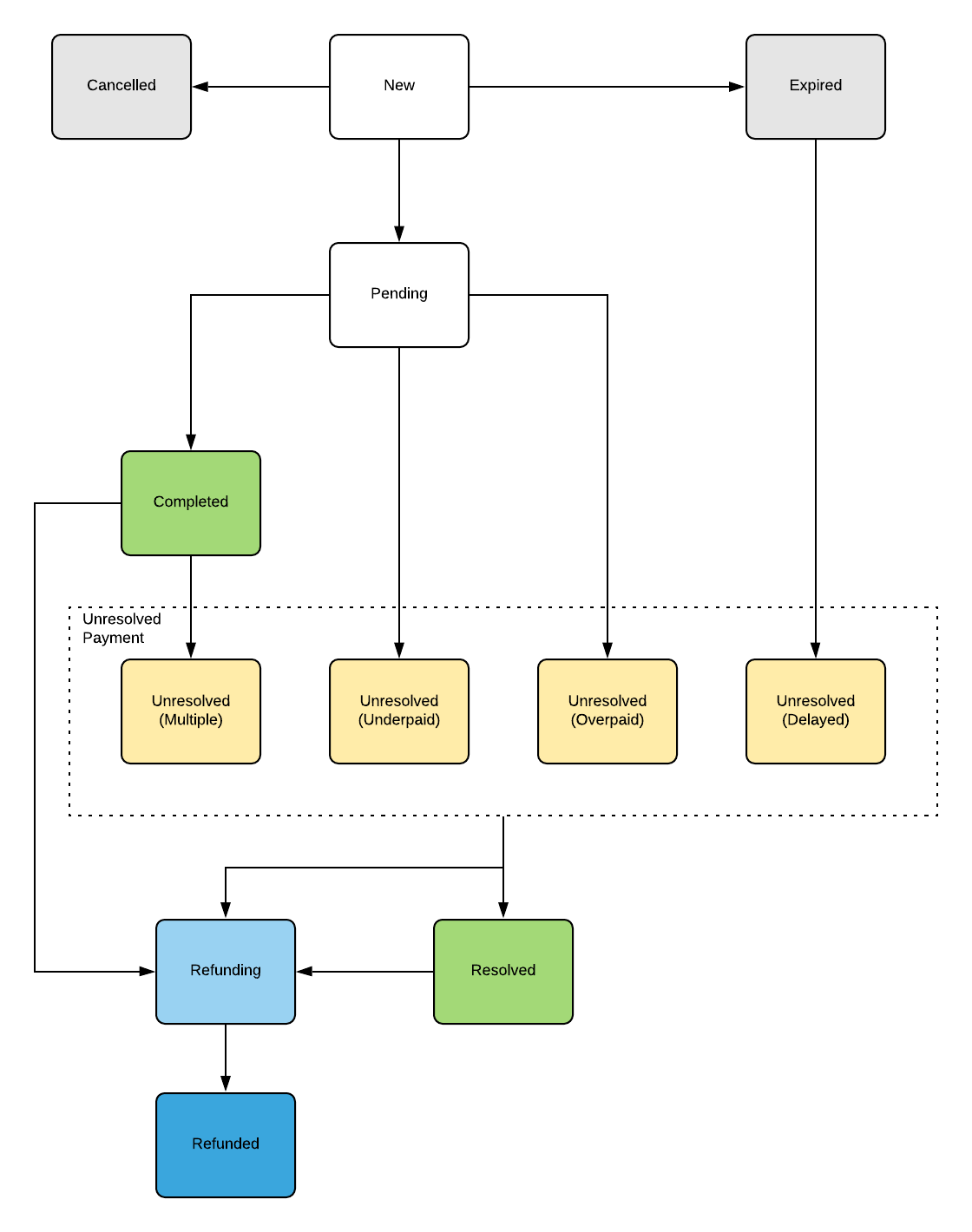
Coinbase Payment Flow (courtesy of Coinbase)
Initial Setup
Coinbase Commerce Account
💡 Although not required, it is a good idea to have a personal Coinbase Account with ETH or BTC available for small test payments. Currently, Coinbase has no sandbox 🙄, so you need to make real payments to test your integration.
Sign up for a Coinbase Commerce account.
Create an API key and make a note of the Webhook signing secret - they will be needed in the next section.
Coinbase API keys
Cloud Functions
Cloud functions are required to (1) create a payment intent charge, and to (2) listen to webhooks that are fired when the payment is sent and confirmed on the blockchain. Coinbase has a Node SDK to simplify the integration.
firebase init functions
cd functions
npm install coinbase-commerce-node cors
# If using TypeScript use these types
npm install @types/coinbase-commerce-node --save-dev
Import the required packages:
const functions = require('firebase-functions');
const cors = require('cors')({ origin: '*' });
const { Client, Webhook, resources } = require('coinbase-commerce-node');
const coinbaseSecret = 'your-api-key';
const signingSecret = 'your-webhook-secret';
Client.init(coinbaseSecret);
const { Charge } = resources;
Backend
Create a Charge
Create a charge with the amount and product details. This demo uses a static product in an HTTP cloud function, but you likely want to pass custom data via the request body. The resulting charge object provides a hosted_url field that can be shown to the end user where they can choose their preferred coin for payment.
exports.createCharge = functions.https.onRequest((req, res) => {
cors(req, res, async () => {
// TODO get real product data from database
const chargeData = {
name: 'Widget',
description: 'Useless widget created by Fireship',
local_price: {
amount: 9.99,
currency: 'USD',
},
pricing_type: 'fixed_price',
metadata: {
user: 'jeffd23',
},
};
const charge = await Charge.create(chargeData);
console.log(charge);
res.send(charge);
});
});
Handle Webhooks
When the transaction’s status changes on the blockchain, Coinbase will send a webhook (event) to your server.
pendingmeans the user has submitted a payment, but it’s not confirmed on the blockchain yet.confirmedpayment is completed. OK to ship.failedpayment failed. Do NOT ship.
For security, it’s essential to call Webhook.verifyEventBody with your webhook secret from Coinbase dashboard. Without this step, a hacker could pretend to be Coinbase and send webhooks to your server.
Create another HTTP cloud function to handle webhooks.
exports.webhookHandler = functions.https.onRequest(async (req, res) => {
const rawBody = req.rawBody;
const signature = req.headers['x-cc-webhook-signature'];
try {
const event = Webhook.verifyEventBody(rawBody, signature, signingSecret);
functions.logger.info(event);
if (event.type === 'charge:pending') {
// TODO
// user paid, but transaction not confirm on blockchain yet
}
if (event.type === 'charge:confirmed') {
// TODO
// all good, charge confirmed
}
if (event.type === 'charge:failed') {
// TODO
// charge failed or expired
}
res.send(`success ${event.id}`);
} catch (error) {
functions.logger.error(error);
res.status(400).send('failure!');
}
});
Serve or Deploy the Functions
firebase serve
# Deployment required to handle webhooks
firebase deploy
Frontend
Fetch with Vanilla JS
The frontend code needs to make a request to the cloud function to create a charge. When the charge object is available, it can redirect or display a link to the hosted payment page.
<button id="btn">Buy Something with Crypto</button>
<p id="pay"></p>
<script>
const btn = document.getElementById('btn');
const pay = document.getElementById('pay');
btn.onclick = async() => {
const res = await fetch('http://localhost:5000/friendly-demos/us-central1/createCharge');
const charge = await res.json();
console.log(charge);
pay.innerHTML = `<a href="${charge.hosted_url}">Pay Now!</a>`
}
</script>